[ad_1]
The Cambrian-Ordovician aquifer system ranks ninth in the nation as a source of groundwater for public supply, providing 631 million gallons per day for this use. The aquifer underlies an area with a population of about 26 million people in parts of seven states and includes the metropolitan areas of Chicago, Illinois; Milwaukee, Wisconsin; and Minneapolis-St. Paul, Minnesota.
USGS scientists tested for hundreds of water-quality constituents and characteristics in samples of untreated groundwater from 60 public-supply wells throughout the aquifer. Results were compared to human-health benchmarks.
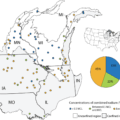
Results show one or more inorganic constituents present at high concentrations, meaning at levels exceeding human-health benchmarks, in groundwater in about 50 percent of the study area. Manmade organic constituents, which include pesticides and volatile organic compounds, were not detected at high concentrations.
Many inorganic constituents, including trace elements and radioactive constituents, occur naturally in groundwater, although concentrations can be affected by human activities. Radioactive constituents were present at high levels in groundwater in about 45 percent of the study area. Most of the radioactivity in groundwater comes from the decay of isotopes of uranium and thorium that are naturally present in minerals found in aquifers. Other inorganic constituents, notably strontium, arsenic and fluoride, were detected at high levels in groundwater in about 12 percent of the study area.
“Nuisance” constituents—those that can affect water’s taste, color or odor—were present at high levels, meaning they exceeded the Environmental Protection Agency’s non-mandatory benchmarks, in 63 percent of the study area. Total dissolved solids, a measure of the salinity of groundwater, occurred at high levels in groundwater in 40 percent of the study area.
Groundwater provides nearly half of the nation’s drinking water. To help protect this vital resource, the USGS National Water-Quality Assessment, or NAWQA, Project of the National Water Quality Program assesses groundwater quality in aquifers that are important sources of drinking water.
Over the last two decades, USGS scientists have assessed water quality in untreated water from 6,600 wells in extensive regional aquifers that supply most of the groundwater pumped for the nation’s drinking water, irrigation and other uses. This comprehensive sampling, along with detailed information on geology, hydrology, geochemistry and chemical and water use, can be used to explain how and why aquifer vulnerability to contamination varies across the nation.
Between 2013 and 2023, NAWQA will continue to assess the quality of the nation’s groundwater by sampling about 2,300 shallow wells and 1,400 deep public-supply wells for a broad range of water-quality constituents. USGS-led national- and regional-scale modeling will provide a three-dimensional perspective of the quality of the nation’s groundwater. In conjunction, the data and modeling can be used to inform management decisions. More information on USGS regional aquifer assessments can be found in a previous USGS Featured Story.
To learn more, visit these websites:
USGS National Summary Circular, Quality of the Nation’s Groundwater Quality, 1991-2010
Regional reports on principal aquifers of the U.S.
National Water-Quality Assessment (NAWQA) Project
USGS Groundwater Information
WaterSMART
[ad_2]
Source link
- Warmer water could cool Montana’s trout fishing economy - September 7, 2022
- Water Released from Crystallizing Magma can Trigger Earthquakes in Yellowstone - September 5, 2022
- Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing at Yellowstone 101 - August 29, 2022